Safety Erudite Inc.
Contractor Safety Management
Comprehensive Contractor Safety Management Solutions for Various Industries
Learn More
Contractors face workplace injuries at rates 3-4 times higher than regular employees, highlighting the urgent need for specialized safety measures tailored to contractor management. At Safety Erudite Inc, we offer robust Contractor Safety Management Processes designed to address these challenges and ensure safety across multiple industries. Below, we provide an in-depth look at our services and their benefits for sectors such as oil and gas, power, manufacturing, agriculture, transportation, construction, mining, and quality management.
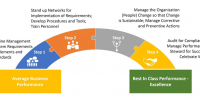
Building a Fit-for-Purpose Contractor Safety Management Process for the Organization
Learn More
Custom-Tailored Safety Frameworks:
Hazard Identification and Risk Assessment:
- Site Inspections: Conduct comprehensive on-site evaluations to identify potential hazards specific to the worksite. This includes assessing environmental conditions, reviewing site layout, and pinpointing potential safety concerns related to contractor activities.
- Task Analysis: Break down contractor tasks into detailed steps to understand specific risk points and interactions between tasks. This analysis helps identify areas where hazards may arise and where safety controls need to be implemented.
- Historical Data Review: Analyze past incident reports, near-misses, and safety audits from similar projects or operations to anticipate and mitigate potential risks. This includes reviewing patterns and root causes of past incidents to prevent recurrence.
Safety Protocol Development:
- Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs): Develop clear, detailed guidelines for safe operations, including step-by-step instructions for routine and non-routine tasks. Ensure SOPs address both general safety and task-specific risks.
- Emergency Response Plans: Create detailed emergency response procedures for various scenarios, including fire, chemical spills, and natural disasters. Plans should outline roles, responsibilities, communication channels, and evacuation routes.
- Safety Manuals: Produce comprehensive documents that cover all aspects of contractor safety, including hazard communication, emergency procedures, and compliance with regulatory requirements. These manuals should be easily accessible and regularly updated.
Integration with Existing Systems:
- Aligning Protocols: Ensure new safety protocols are aligned with and enhance your current safety management systems. This includes integrating new procedures with existing safety workflows and compliance checks.
- System Compatibility: Implement safety tools and technologies that are compatible with your existing software and reporting systems. Ensure seamless data sharing and reporting between new and existing systems.
- Continuous Feedback Loop: Establish mechanisms for ongoing feedback and continuous improvement. This includes setting up regular review meetings, safety performance metrics, and adaptation processes to address emerging safety needs.
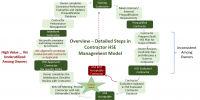
Developing Tools and Processes for Each Stage of Contractor Safety Management
Learn More
Comprehensive Safety Tools and Procedures:
Pre-Qualification Tools:
- Safety Performance Scorecards: Assess historical safety performance and compliance with industry standards. Scorecards evaluate metrics such as incident rates, compliance history, and previous safety improvements.
- Certification Checklists: Verify that contractors hold necessary safety certifications and training. This includes checking credentials for specialized training, industry certifications, and compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Risk Assessments: Evaluate contractor-specific risks based on their previous work and safety records. This assessment helps identify potential risks associated with the contractor’s work history and project-specific challenges.
Onboarding Processes:
- Safety Orientations: Provide comprehensive briefings on site-specific hazards, safety protocols, and emergency procedures. Orientations should include site tours, introductions to key personnel, and detailed explanations of safety practices.
- Training Sessions: Conduct detailed training on safety equipment, emergency procedures, and operational protocols. Training should be interactive and tailored to the specific needs of the contractors and their tasks.
- Digital Resources: Offer access to online safety handbooks, training modules, and other digital resources for continuous learning. Ensure that resources are regularly updated and easily accessible.
Ongoing Monitoring Systems:
- Real-Time Tracking: Implement systems to monitor contractor activities and safety compliance in real-time. Use technologies such as GPS, wearable sensors, and compliance tracking software to ensure continuous oversight.
- Regular Audits: Schedule routine safety audits and inspections to assess adherence to safety protocols. Audits should be systematic, involving checklists, interviews, and on-site evaluations.
- Performance Reviews: Conduct periodic reviews to evaluate contractor performance and address safety concerns. Reviews should include feedback from supervisors, incident reports, and compliance assessments.
Incident Management Procedures:
- Incident Reporting Systems: Develop systems for prompt and accurate reporting of safety incidents. Ensure that reporting systems are user-friendly and provide real-time alerts to relevant personnel.
- Investigation Procedures: Establish clear procedures for investigating incidents, including root cause analysis and corrective actions. Procedures should involve detailed documentation and follow-up to prevent recurrence.
- Documentation Practices: Ensure thorough documentation of incidents and responses for regulatory compliance and future reference. Maintain detailed records of incident reports, investigations, and corrective actions.
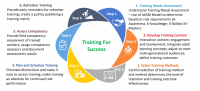
Training Workers on Contractor Safety Management Principles
Learn More
Interactive and Practical Training:
Safety Protocol Education:
- Hazard Controls: Provide training on identifying and managing hazards specific to contractor tasks. This includes instruction on hazard recognition, control measures, and the use of safety equipment.
- Safety Equipment Use: Train workers on the proper use of personal protective equipment (PPE) and safety tools. Emphasize the importance of correct equipment usage and maintenance.
- Emergency Procedures: Educate workers on emergency response protocols, including evacuation procedures, first aid, and communication during emergencies.
Risk Awareness Workshops:
- Real-Life Scenarios: Use case studies and simulations to illustrate potential hazards and effective safety practices. Workshops should include interactive discussions and problem-solving exercises.
- Interactive Exercises: Engage participants in activities that reinforce risk management strategies and emergency response skills. Exercises should be hands-on and relevant to the specific tasks contractors perform.
- Feedback Sessions: Provide opportunities for participants to discuss safety concerns and provide feedback on protocols. Use feedback to refine training programs and address emerging safety issues.
Emergency Response Drills:
- Scenario-Based Drills: Conduct simulations of potential emergency situations to test response protocols. Drills should cover a range of scenarios relevant to the work environment.
- Coordination Exercises: Organize drills designed to improve coordination and communication among team members during emergencies. Focus on teamwork, leadership, and effective communication.
- Performance Evaluation: Assess drill performance to identify areas for improvement and refine emergency procedures. Use evaluations to enhance training programs and emergency response plans.
Developing Leading KPIs for Stewardship of Contractor Safety Performance
Learn More
Proactive Safety Management through KPIs:
Measure Safety Performance:
- Safety Audit Results: Track metrics on the frequency and outcomes of safety audits, including compliance rates and identified issues. Use audit results to assess overall safety performance and identify areas for improvement.
- Compliance Rates: Monitor rates of adherence to safety protocols and regulations. Evaluate compliance with safety procedures, training requirements, and regulatory standards.
- Safety Meeting Frequencies: Measure the frequency and effectiveness of safety meetings and briefings. Ensure regular meetings are held and address relevant safety topics.
Identify Trends and Potential Issues:
- Data Analysis: Examine trends in safety performance, incident rates, and compliance metrics. Use data analysis to identify patterns, potential issues, and areas for improvement.
- Predictive Analytics: Utilize predictive analytics to forecast potential safety issues and implement preventive measures. Analyze historical data to anticipate and mitigate future risks.
- Trend Reports: Regularly review KPI reports to identify emerging risks and safety trends. Use reports to inform decision-making and adjust safety protocols as needed.
Drive Continuous Improvement:
- Performance Reviews: Regularly review KPI data to assess the effectiveness of safety protocols and make necessary adjustments. Use performance reviews to refine safety measures and enhance outcomes.
- Action Plans: Develop action plans based on KPI insights to address identified issues and improve safety measures. Implement corrective actions and track progress.
- Benchmarking: Compare KPI performance against industry standards to set and achieve safety improvement goals. Use benchmarking to identify best practices and enhance safety performance.
Benefit of contractor safety management in different industries
Learn More
Contractor safety management is crucial across various industries due to the unique risks and operational demands each sector presents. Implementing effective contractor safety management practices can yield significant benefits, enhancing overall safety, productivity, and compliance.
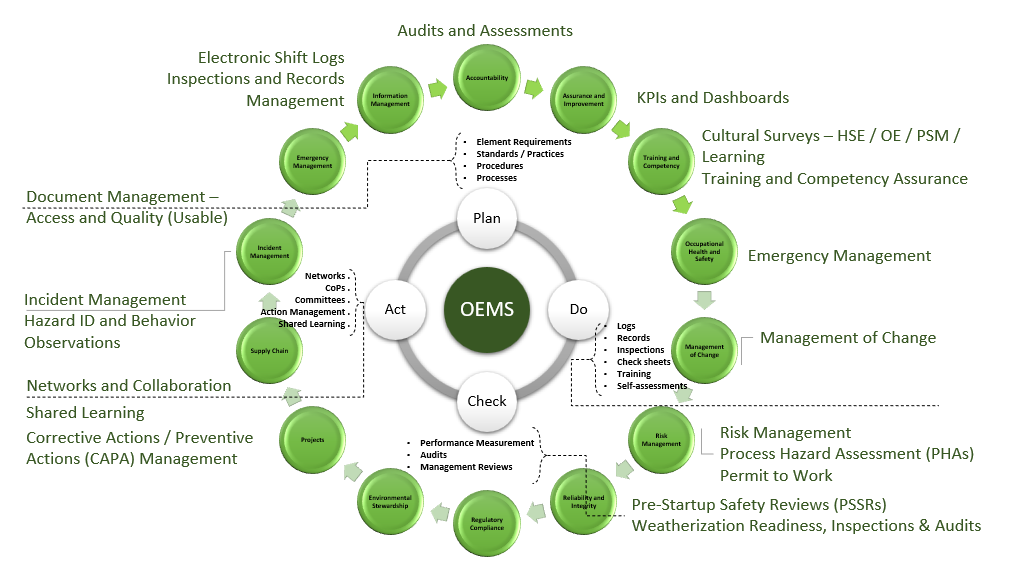
The Integrated Management Systems Provider – EHS, PSM, OEMS
Safety Erudite Inc. is a leading North American provider of Integrated Management Systems for energy and manufacturing industries. We collaborate with clients to implement right-sized Environmental Health and Safety (EHS), Process Safety Management (PSM), and Operations Excellence Management Systems (OEMS)
Contact
Email
customersupport@safetyerudite.com
Office Number
+1(469) 353-9974
Office Address
Canada
112 Sherwood Lane NW Calgary, AB, T3R OV3, Canada
USA
201 Long Canyon Court Richardson TX, 75080, USA