Safety Erudite Inc.
Training And Competency Assurance Management
Understanding the Limitations of Sheep Dipping
Learn More
The Flaws in Traditional Training Methods
In many organizations, especially those dealing with high-risk environments, the effectiveness of training can significantly impact safety and operational success. One common approach, known as “Sheep Dipping,” applies the same training program uniformly across all employees. While this method may seem efficient at first glance, it comes with several notable limitations that can hinder organizational performance and safety.
Lack of Role Relevance
One of the primary issues with Sheep Dipping is its lack of relevance to specific job roles. When all employees receive the same training content, it often fails to address the unique requirements and responsibilities of different positions. For example, a safety officer and a maintenance technician have vastly different roles and challenges. Training designed for one may not be effective for the other, leading to a disconnect between the training provided and the actual skills needed.
Resource Inefficiency
Sheep Dipping also leads to inefficient use of resources. Training programs that cover generic content may not be valuable for every employee. This results in wasted time and resources as employees are exposed to information that may not be applicable to their specific duties. For instance, an advanced safety protocol training might be unnecessary for employees whose primary role involves basic awareness of safety practices.
Inadequate Skill Development
Another significant drawback is the lack of depth in skill development. Generic training programs might not provide the advanced skills needed for specialized or leadership roles. For example, a Subject Matter Expert (SME) requires in-depth knowledge and problem-solving skills beyond what a basic training program can offer. Without targeted training, employees in advanced roles may not develop the necessary expertise to handle complex tasks effectively.
The Need for a Tailored Approach
Given these limitations, it’s clear that a one-size-fits-all approach to training is often insufficient. Organizations need to move beyond Sheep Dipping and adopt training methods that are tailored to the specific needs of different roles. In the following articles, we’ll explore how to implement a more effective, competency-based training approach that ensures each employee receives the training they need to excel in their role.
Implementing a Competency-Based Training Approach
Learn More
A Strategic Shift for Effective Training
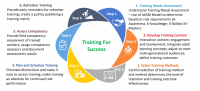
To overcome the limitations of Sheep Dipping, organizations must embrace a competency-based training approach. This method focuses on aligning training programs with the specific requirements of safety-critical roles, ensuring that each employee receives the relevant skills and knowledge needed for their job. Here’s how to implement this approach effectively:
Defining Safety-Critical Roles and Proficiency Levels
The first step in a competency-based approach is to clearly define safety-critical roles within the organization. These roles are those where an employee’s competence directly affects safety and operational success. For instance, emergency response teams and safety auditors are roles that require specific and advanced training.
The AKSM Model provides a useful framework for categorizing proficiency levels:
- A – Awareness: This level provides basic information about safety practices and organizational policies. It is suitable for employees who need to understand general safety principles without delving into technical details.
- K – Knowledge: At this level, training includes in-depth knowledge required for specific tasks. Employees learn how to perform their duties safely and efficiently, including the use of equipment and adherence to procedures.
- S – Subject Matter Expert: This level is for employees who need advanced expertise in a particular area. They are responsible for troubleshooting complex issues, guiding others, and implementing best practices based on their specialized knowledge.
- M – Mastery: The highest level of training involves not just performing tasks expertly but also leading, innovating, and shaping safety practices and policies. Mastery-level employees contribute to the development of training programs and safety standards.
Performing Comprehensive Training Needs Assessments
Once roles and proficiency levels are defined, the next step is to conduct detailed training needs assessments. This involves evaluating the current skills and knowledge of individual employees, workgroups, and the organization as a whole.
- Individual Assessments: Evaluate each employee’s current skill level and identify specific areas for development. This can be done through performance reviews, practical tests, and self-assessments.
- Group Assessments: Analyze the collective capabilities of teams or departments to identify gaps that could impact performance and safety. This ensures that training programs address both individual and team needs.
- Organizational Assessment: Examine the overall training needs of the organization, considering factors such as industry changes, new technologies, and evolving regulations. This helps ensure that the entire organization remains up-to-date with required competencies.
Based on the assessments, develop tailored training programs that address the unique needs of each role and individual. This approach ensures that training is relevant and effective, leading to better performance and safety outcomes.
Developing Gap Closure and Competency Maintenance Plans
Learn More
Ensuring Continuous Improvement and Readiness
A key component of a competency-based training approach is developing plans to address gaps in skills and maintain competencies over time. This involves creating targeted training interventions and strategies for ongoing development.
- Targeted Training: Develop specific training interventions to address identified gaps. For instance, if a team lacks proficiency in using new safety equipment, create a specialized training module to bridge this gap.
- Mentoring and Coaching: Pair employees with experienced mentors or coaches who can provide personalized guidance and support. This helps in transferring practical knowledge and experience that goes beyond formal training.
- Development Plans: Create individualized development plans for employees based on their assessed needs. These plans should include goals, timelines, and resources needed to achieve the desired competencies.
Competency Maintenance Strategies
- Refresher Courses: Schedule regular refresher courses to help employees maintain their skills and stay updated on new practices and regulations. For example, annual refresher courses on emergency procedures can help keep employees prepared for potential incidents.
- Continuous Development: Encourage ongoing learning through advanced training opportunities, industry certifications, and professional development initiatives. This ensures that employees remain adaptable and up-to-date with advancements in their field.
- Performance Reviews: Conduct regular performance reviews to assess the effectiveness of training and development efforts. Use this feedback to make necessary adjustments to training programs and development plans.
Creating a Culture of Continuous Improvement
Promote a culture of continuous improvement by encouraging employees to seek out learning opportunities and provide feedback on training programs. This helps ensure that training remains relevant and effective in meeting the evolving needs of the organization.
Monitoring and Evaluating Training Effectiveness
Learn More
Ensuring Training Programs Deliver Results
Monitoring and evaluating the effectiveness of training programs is essential to ensure that they achieve their intended goals and contribute to overall organizational success. Here’s how to effectively track and assess training outcomes:
Tracking Progress
- Performance Metrics: Utilize various performance metrics to measure the impact of training programs. This can include tracking incident rates, performance evaluations, and completion rates for training modules. For example, monitoring the number of safety incidents before and after training can provide insights into its effectiveness.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Collect feedback from employees and supervisors to assess the relevance and quality of the training. Surveys, interviews, and focus groups can provide valuable input on how well training programs are meeting their needs and where improvements might be needed.
Adapting Training Programs
- Iterative Improvement: Regularly review training programs based on performance data and feedback. Make necessary updates to ensure that training remains effective and relevant to current needs. This iterative process helps in refining training content and methods to better address emerging challenges.
- Flexibility: Ensure that training programs can adapt to changes in industry standards, technological advancements, and regulatory requirements. This flexibility helps maintain a competent and up-to-date workforce capable of handling evolving demands.
Reporting and Accountability
- Training Reports: Develop comprehensive reports that summarize the effectiveness of training programs. Include data on performance improvements, feedback received, and any adjustments made to training content or methods.
- Accountability: Establish accountability measures to ensure that training programs are implemented effectively and that employees complete required training. This can include tracking compliance and addressing any issues related to training participation or effectiveness.
The Integrated Management Systems Provider – EHS, PSM, OEMS
Safety Erudite Inc. is a leading North American provider of Integrated Management Systems for energy and manufacturing industries. We collaborate with clients to implement right-sized Environmental Health and Safety (EHS), Process Safety Management (PSM), and Operations Excellence Management Systems (OEMS)
Contact
Email
customersupport@safetyerudite.com
Office Number
+1(469) 353-9974
Office Address
Canada
112 Sherwood Lane NW Calgary, AB, T3R OV3, Canada
USA
201 Long Canyon Court Richardson TX, 75080, USA